P0184 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Intermittent: Diagnosis and Solutions
P0184 is a generic diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to the powertrain, applicable to most OBD-II equipped vehicles (Nissan, Ford, Fiat, Chevrolet, Toyota, Dodge, etc.). It indicates that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has detected an intermittent or erratic voltage signal from the Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” circuit. This fault can impact the air-fuel mixture calculation and engine performance.
Understanding the P0184 Code
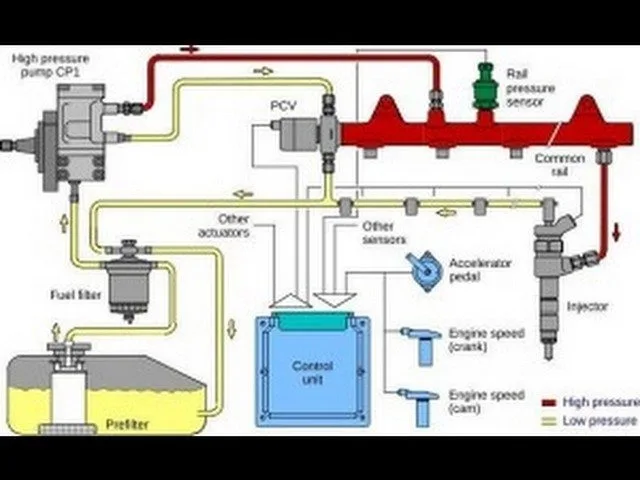
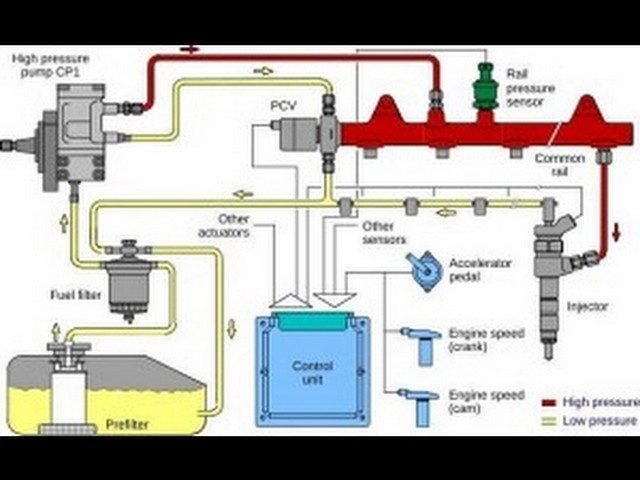
The fuel temperature sensor is typically integrated within the fuel composition sensor, located between the fuel tank and the fuel rail. Its role is crucial: it analyzes the fuel composition (ethanol percentage, water presence) and measures its temperature. The PCM uses this data, transmitted as electrical signals and waveforms, to precisely adjust the injection strategy, especially on flex-fuel vehicles. An intermittent signal disrupts these calculations and triggers the P0184 code.
Symptoms of the P0184 Code
The severity of this code is moderate to severe, as it can affect fuel consumption and performance. Symptoms include:
- Illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the dashboard.
- Decreased engine performance or engine hesitation/misfires.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Possible presence of other codes related to fuel composition.
- Sometimes, no obvious symptoms are noticeable.
Possible Causes of the P0184 Fault
Several elements can be the origin of this fault code:
- Electrical Problems: Shorted, damaged, corroded, or loose wires, wiring, or connectors in the circuit.
- Faulty Sensor: The fuel temperature/composition sensor itself is malfunctioning.
- Related Sensors: A faulty intake air temperature sensor or an ambient air temperature sensor can send conflicting data.
- PCM Failure: A programming error or internal failure of the control module (less common).
Diagnostic and Repair Procedures
Before starting, consult the manufacturer’s Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) to check if the problem is subject to a recall or a specific procedure.
- Visual Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the wiring harness and connectors associated with the sensor. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or burning.
- Clearing Codes: After any minor repair (e.g., tightening a connector), clear the codes and drive the vehicle to see if the fault reappears.
- Electrical Test (DVOM): Using a Digital Volt-Ohm Meter (DVOM), check for the presence of the reference voltage (usually 5V) and ground at the sensor connector. Absence of voltage may indicate a wiring problem or, as a last resort, a faulty PCM.
- Sensor Test: Measure the sensor’s resistance and compare it to the manufacturer’s specified values. Always disconnect the PCM before these tests to avoid damaging it.
- Advanced Analysis (Oscilloscope): For precise diagnosis, use an oscilloscope to observe the signal waveform. Compare the displayed fuel temperature with an actual measurement taken using an infrared thermometer. A discrepancy indicates a faulty sensor.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Diagnosing a P0184 code requires a methodical approach, starting with the simplest checks. Although some symptoms may be subtle, do not ignore this code at the risk of encountering performance and consumption issues. If the diagnostic procedures are beyond your skills, consult a professional mechanic equipped with the necessary tools and technical data for a reliable and lasting repair.