1. Introduction
DF (Manufacturer Defect) codes are specific to Renault vehicles. They help identify technical anomalies using diagnostic tools like the CanClip diagnostic tool.
2. Structure of DF Codes
| Format | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| DFXXX | DF025 | Unique code with 3 digits |
| DFXXXX | DF1001 | Extended code for recent models |
Severity Icon Legend:
- 🟢 Low : Minor issue, can be postponed.
- 🟠 Medium : Serious problem, but the vehicle can still be driven
- 🔴 High : Critical issue requiring immediate intervention.
3. Codes by System
🔧 Engine
| Code | Description | Possible Causes | Severity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF001 | Coolant temperature sensor circuit | Faulty sensor, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF002 | Air temperature sensor circuit | Faulty sensor, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF004 | Boost pressure sensor circuit | Faulty pressure sensor, leak in the boost system | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF007 | Rail pressure sensor circuit | Faulty rail pressure sensor, fuel pump problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF011 | Sensor supply voltage No.1 | Electrical problem, damaged wiring, ECU failure | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF012 | Sensor supply voltage No.2 | Electrical problem, damaged wiring, ECU failure | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF013 | Sensor supply voltage No.3 | Electrical problem, damaged wiring, ECU failure | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF015 | Main relay control circuit | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF025 | Diagnostic link to glow plug control unit | Communication problem with glow plug control unit, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF026 | Cylinder 1 injector control circuit | Faulty injector, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF027 | Cylinder 2 injector control circuit | Faulty injector, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF028 | Cylinder 3 injector control circuit | Faulty injector, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF029 | Cylinder 4 injector control circuit | Faulty injector, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF032 | Glow plug relay 1 control circuit | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF033 | Glow plug relay 2 control circuit | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF034 | Glow plug relay 3 control circuit | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, connection problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF038 | ECU | ECU failure, communication problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF047 | ECU supply voltage | Electrical problem, damaged wiring, battery failure | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF050 | Brake switch circuit | Faulty brake switch, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF051 | Cruise control / speed limiter function | Cruise control problem, faulty speed sensor | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF052 | Injector control circuit | Wiring problem, injector failure | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF053 | Rail pressure regulation function | Pressure regulation problem, faulty rail pressure sensor | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF054 | Boost solenoid valve control circuit | Faulty solenoid valve, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF056 | Air flow sensor circuit | Faulty air flow sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF090 | Vehicle speed sensor circuit | Faulty speed sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF098 | Fuel temperature sensor circuit | Faulty fuel temperature sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF101 | Multiplexed trajectory control link | Multiplex communication problem, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF120 | Engine speed sensor signal | Faulty engine speed sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF195 | Camshaft / engine speed sensor consistency | Synchronization problem between camshaft sensor and speed sensor | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF200 | Atmospheric pressure sensor | Faulty atmospheric pressure sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF201 | Air flow sensor information | Faulty air flow sensor, communication problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF209 | EGR valve position sensor circuit | Faulty EGR position sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF272 | EGR valve control circuit | Faulty EGR valve, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF293 | Water in diesel detector | Water presence in fuel, faulty sensor | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF297 | Particulate filter | Clogged or faulty particulate filter | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF304 | EGR bypass circuit | EGR bypass problem, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF310 | Upstream particulate filter temperature sensor | Faulty temperature sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF319 | Camshaft sensor circuit | Faulty camshaft sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF323 | Air intake flap | Blocked or faulty air intake flap | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF342 | MIL indicator circuit | Electrical problem, faulty MIL indicator | 🟢 Low | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF374 | ECU | ECU failure, communication problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF394 | Catalyst functional failure | Faulty catalyst, exhaust gas regulation problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF409 | Fuel level sensor circuit | Faulty fuel level sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF532 | Alternator load information | Faulty alternator, charging problem, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF559 | Low speed GMV relay control | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF567 | ECU | ECU failure, communication problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF569 | Boost circuit | Boost problem, faulty turbo | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF619 | EGR valve stuck open | Stuck EGR valve, mechanical or electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF631 | Brake light switch information | Faulty brake light switch, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF641 | Air intake flap circuit | Blocked or faulty air flap, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF644 | Fuel flow regulator circuit | Faulty flow regulator, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF645 | Air intake flap position regulation | Faulty intake flap, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF646 | Air intake flap position sensor | Faulty position sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF647 | EGR valve position regulation | Faulty EGR valve, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF648 | ECU | ECU failure, communication problem | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF651 | Upstream turbine pressure sensor circuit | Faulty pressure sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF652 | Upstream turbine temperature sensor circuit | Faulty temperature sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF653 | Cylinder No.1 fuel injection calibration | Injector calibration problem, faulty injector | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF654 | Cylinder No.2 fuel injection calibration | Injector calibration problem, faulty injector | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF655 | Cylinder No.3 fuel injection calibration | Injector calibration problem, faulty injector | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF656 | Cylinder No.4 fuel injection calibration | Injector calibration problem, faulty injector | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF721 | Engine overheating | Cooling problem, faulty temperature sensor | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF771 | Flow regulation adaptive | Flow regulation problem, faulty sensor | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF778 | Upstream turbine temperature regulation | Faulty temperature sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF885 | Rail pressure | Faulty pressure sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF887 | Brake / accelerator pedal position | Faulty position sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF897 | Pump pressure regulator circuit | Faulty pressure regulator, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF974 | Pedal potentiometer track 1 circuit | Faulty potentiometer, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF975 | Pedal potentiometer track 2 circuit | Faulty potentiometer, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF987 | Cruise control / speed limiter buttons | Faulty buttons, damaged wiring, communication problem | 🟢 Low | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF991 | Particulate filter injector control circuit | Faulty injector, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF992 | Heating resistor relay 1 control | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF993 | Heating resistor relay 2 control | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF994 | Heating resistor relay 3 control | Faulty relay, damaged wiring, electrical problem | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF997 | Glow plug control unit link | Communication problem, damaged wiring, faulty module | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF998 | Upstream turbine pressure | Faulty pressure sensor, damaged wiring | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1001 | Upstream particulate filter temperature regulation | Faulty temperature sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1012 | Multiplexed information consistency for RV / LV | CAN communication problem, damaged wiring, faulty module | 🔴 High | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1013 | Cruise control input monitoring | Communication problem, faulty sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1014 | Vehicle speed consistency | Faulty speed sensor, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1015 | Brake contact information consistency | Faulty brake contact, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DF1016 | Clutch contact information consistency | Faulty clutch contact, damaged wiring | 🟠 Medium

Error C1513: Diagnosing and Repairing a Faulty Power SteeringElectric Power Steering (EPS) is a key system in modern vehicles. When the C1513 code appears, it indicates a malfunction in the torque sensor or the electric steering motor. This can be an expensive problem at a garage (€500 to €1500), so here’s how to fix it yourself. 🔍 Common Symptoms
🚗 Most Affected Vehicles
🛠️ Step-by-Step Diagnosis1. Reading the C1513 Code with an OBD2 Scanner
2. Checking the Torque Sensor
3. Inspecting the Electric Steering Motor
4. Checking the CAN Bus Network
5. Checking Connectors and Wiring
💡 Cost-Effective Repair Solutions1. Replacing the Torque Sensor
2. Repairing the Electric Motor
3. Buying a Used EPS Module
⚠️ Mistakes to Avoid
📊 Cost Comparison
🛑 Practical Cases
❓ FAQ
🔧 Recommended Tools

Code P0442: Repairing an Evaporation System Leak YourselfThe P0442 code (“Evaporative System Leak Detected“) is one of the most common OBD-II faults. Often related to a loose gas cap or a faulty canister, this problem can cost €150 to €400 at a repair shop. Here’s how to fix it for less than €50. 🔍 P0442 Symptoms
🚗 Most Affected Vehicles
🛠️ Step-by-Step Diagnosis1. Gas Cap Check
2. EVAP System Leak Test
3. Charcoal Canister Inspection
4. Purge Valve Check
💡 Economical DIY Repairs1. Replace the Gas Cap
2. Repair the Charcoal Canister
3. Clean the Purge Valve
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid
📊 Comparative Costs
🛑 Case Studies
❓ FAQ
🔧 Recommended Tools
🚨 Safety Warning
Intermittent OBD Codes: Pro Methods for Diagnosing Ghost Failures1. Introduction
2. Common Causes of Intermittent Codes
3. Essential Tools
4. Diagnostic Methods
5. Practical Cases
6. FAQ
7. Mistakes to Avoid
Additional SEO Tips
Advanced Diagnostics with UDS (Unified Diagnostic Services): Everything You Need to Know About Modern Vehicle Protocol1. Introduction
2. UDS vs OBD-II: Key Differences
3. Essential Tools for UDS
4. Decoding UDS Codes
5. Practical Cases
6. Security and Access
7. FAQ
8. Tips for Beginners
SEO Optimization
Proposed Infographic
Code P0128 (Thermostat Stuck Open): Symptoms, Risks, and Cost-Effective RepairThe fault code P0128 indicates a problem with engine temperature regulation, often related to a thermostat stuck in the open position. This malfunction prevents the engine from reaching its optimal temperature, impacting performance, fuel consumption, and longevity. Discover how to identify, repair, and avoid risks at a lower cost. Symptoms of a Stuck Open Thermostat (P0128)
Risks of Ignoring a P0128 Code
Causes of the P0128 Code
Cost-Effective Repair in 4 Steps1. Confirm the Diagnosis
2. Test the Thermostat
3. Replace the Thermostat (Cost: €50 to €150)
4. Check the Temperature Sensor
FAQ: Saving on P0128 RepairQ: Can you drive with a stuck open thermostat? Q: OEM or aftermarket thermostat? Q: P0128 code recurring after replacement? ConclusionA P0128 code should not be ignored, but its repair remains affordable. By replacing the thermostat yourself or opting for an independent garage, you can limit costs to less than €150 in most cases. Act quickly to preserve your engine and avoid more serious breakdowns! Diagnosis of High Voltage Battery Systems in Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive GuideElectric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, and at the heart of this transformation are high-voltage batteries. These batteries are the pillars of electric propulsion, but their diagnosis requires a specific approach and a deep understanding. This article aims to guide you through the complexities of diagnosing high-voltage battery systems, with an emphasis on safety and accuracy. Operation of High-Voltage Batteries A typical high-voltage battery system includes cell modules, a battery management system (BMS), and high-voltage cables. The battery cells, typically lithium-ion, store electrical energy. The BMS plays a crucial role in monitoring and controlling the temperature, voltage, and cell balance, thus ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the battery. Common High-Voltage Battery Error Codes High-voltage battery issues can trigger a variety of specific OBD-II error codes, such as:
Each error code provides valuable information about the nature of the problem, allowing technicians to target their diagnostic efforts. Diagnostic Methods and Required Tools Diagnosing high-voltage battery systems requires specialized tools, including:
Diagnostic procedures include measuring battery voltage, checking isolation, and analyzing BMS data. Essential Safety Precautions Safety is paramount when working on high-voltage battery systems. Here are some essential precautions:
Additional Tips
Conclusion Diagnosing high-voltage battery systems is a complex task that requires technical expertise and constant vigilance. By following safety procedures and using the appropriate tools, technicians can effectively diagnose and repair high-voltage battery issues, ensuring the reliability and safety of electric vehicles. 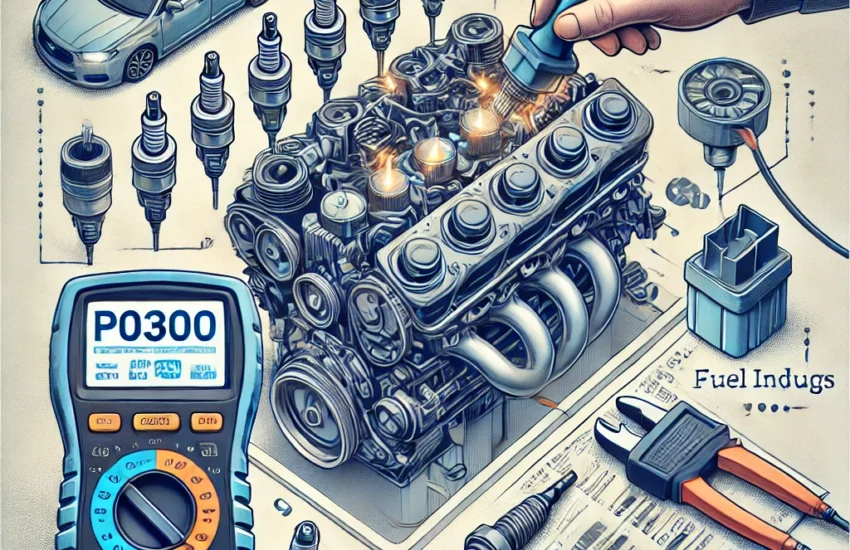
🚨 Code P0300 – Multiple Misfire Detected: Symptoms and Repair📌 What Does Code P0300 Mean?The error code P0300 indicates random misfires in multiple cylinders of the engine. This means the engine is not burning fuel properly, which can lead to power loss, excessive fuel consumption, and engine damage if not repaired promptly. 🚨 Symptoms of Code P0300
⚠️ Possible Causes of Code P0300🔍 The main causes include:
🛠️ How to Fix Code P0300?🔍 1️⃣ Check Spark Plugs and Coils
⛽ 2️⃣ Inspect the Fuel System
⚙️ 3️⃣ Check Engine Compression
🖥️ 4️⃣ Scan and Clear OBD-II Codes
📌 ConclusionCode P0300 is a serious issue that can damage the engine if left untreated. A thorough inspection of the ignition system, fuel system, and engine compression is necessary to identify the exact cause and effectively repair the vehicle. Why do OBD fault codes return after repair?You’ve repaired your vehicle, cleared the OBD fault codes… but the check engine light comes back on! A common problem that frustrates many car owners. In this article, we explain the reasons behind these recurring codes, the mistakes to avoid, and professional solutions to fix them for good. 1. Why Do OBD Codes Return After Repair?
2. Steps to Diagnose a Recurring Code
3. Permanent Solutions to Prevent Recurrence
4. Recommended Tools for Professionals and Enthusiasts
5. FAQ: Common Questions About Recurring OBD Codes
ConclusionRecurring OBD codes are not inevitable! With a methodical approach and the right tools, you can identify the source of the problem and ensure a lasting repair. Consult our OBD code database for detailed explanations of each fault. Introduction to OBD-II Error CodesModern vehicles use the OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) system to monitor engine performance and emissions. When a problem occurs, the system generates an error code, turning on the famous check engine light. Understanding these codes allows drivers to act quickly, avoiding costly repairs. Here is an explanation of the 10 most common OBD-II codes and how to resolve them. 1. P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
2. P0171/P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 1 or 2)
3. P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
4. P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small)
5. P0128 – Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
6. P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
7. P0700 – Transmission Control System Malfunction
8. P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
9. P0507 – Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
10. P0455 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large)
When to Consult a Professional?Some codes, such as those related to the catalytic converter (P0420) or transmission (P0700), often require a mechanic’s intervention. If DIY solutions do not resolve the issue, or if the light flashes (indicating engine risk), go to a garage quickly. Recommended Tools
ConclusionUnderstanding OBD-II codes saves you a lot of stress! Although some repairs are DIY-friendly, do not hesitate to call an expert for complex problems. Find other diagnostic guides on eobdcode.com to maintain your vehicle with confidence. 🚗💡 |